Table of Contents (Click any Topic to view first)
- Syntax of the While Loop:
- Example 1: Simple While Loop
- Example 2: Using While Loop for User Input
- Example 3: While Loop with Conditional Exit
Understanding the While-Loop in Java
In Java programming, the while loop provides a mechanism to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a specified condition remains true. It's particularly useful when the number of iterations is unknown beforehand. Let's dive into the while loop in Java with detailed explanations and examples.
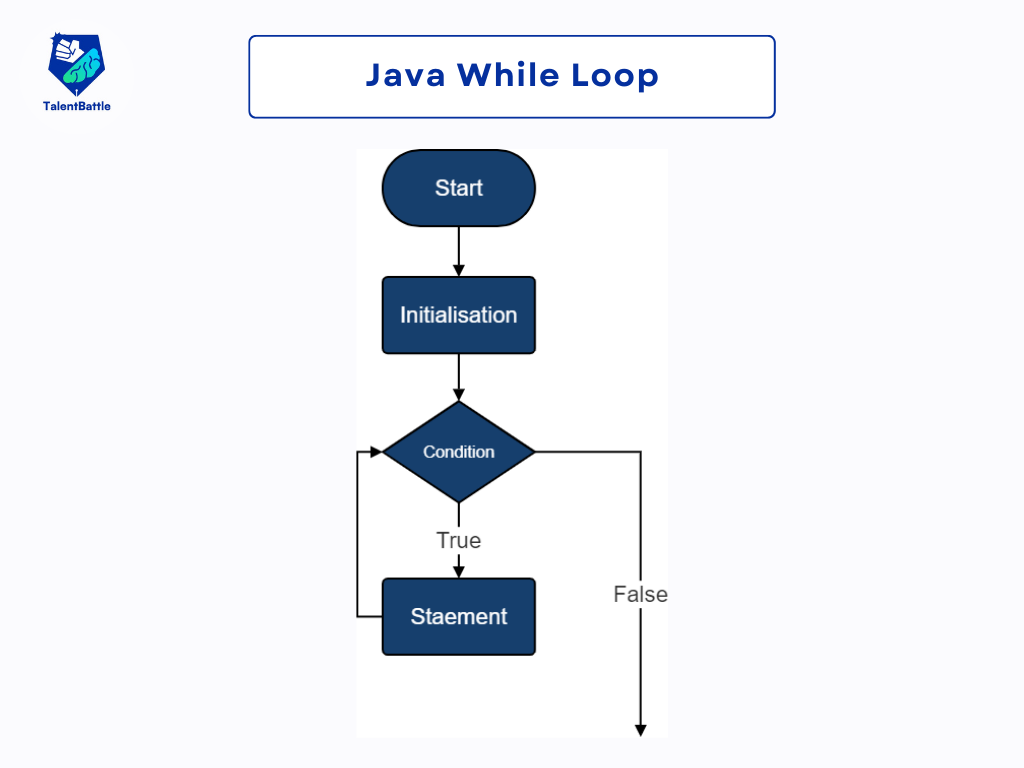
Syntax of the While Loop:
while (condition) {
// Code to be executed
}
The while loop starts by evaluating the condition. If the condition is true, the loop body is executed. After each iteration, the condition is re-evaluated. The loop continues until the condition becomes false.
Example 1: Simple While Loop
public class SimpleWhileLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
System.out.println("Iteration " + i);
i++;
}
}
}
In this example, the while loop executes the block of code inside it as long as the value of i is less than or equal to 5. The loop iterates from 1 to 5, printing each iteration number.
Example 2: Using While Loop for User Input
import java.util.Scanner;
public class WhileLoopUserInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String userInput;
while (true) {
System.out.print("Enter 'exit' to quit: ");
userInput = scanner.nextLine();
if (userInput.equals("exit")) {
break; // Exit the loop if user inputs 'exit'
}
System.out.println("You entered: " + userInput);
}
scanner.close();
}
}
This example demonstrates the use of a while loop for continuous user input. The loop prompts the user to enter text until they input "exit," at which point the loop terminates using a break statement.
Example 3: While Loop with Conditional Exit
public class ConditionalExitWhileLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
System.out.println("Iteration " + i);
if (i == 5) {
break; // Exit the loop when i reaches 5
}
i++;
}
}
}
In this example, the loop iterates from 1 to 10, but it exits prematurely when the value of i becomes 5. This demonstrates how to use a conditional statement inside a while loop to control the loop's behavior.
Conclusion:
The while loop is a fundamental looping construct in Java that allows for iterative execution based on a condition. Whether iterating through a range of values, processing user input, or implementing conditional exits, the while loop provides flexibility and efficiency in program flow control.




